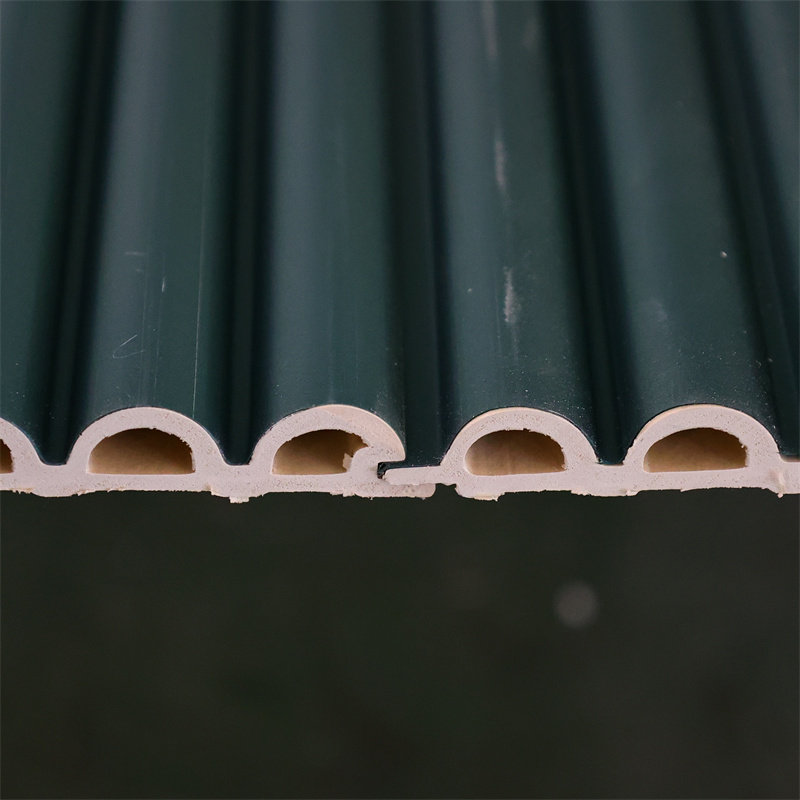

In recent years, the demand for sustainable and eco-friendly building materials has been on the rise,
driven by growing environmental concerns and a shift towards green practices in the construction industry.
Wood-Plastic Composite (WPC) wall panels have emerged as a viable alternative to traditional wall paneling materials due to their eco-friendliness and cost-effectiveness.
This essay delves into the sustainability aspects of WPC wall panels, exploring their environmental impact, economic benefits, and potential contributions to a greener future.
We will also analyze the challenges and opportunities associated with their adoption in the construction sector.
Understanding WPC Wall Panels
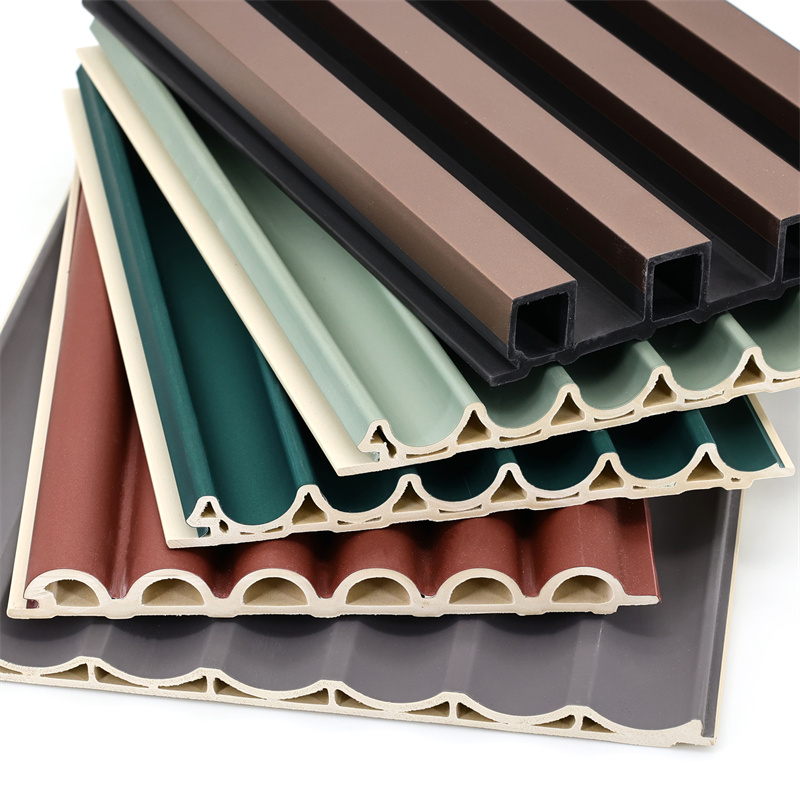
Wood-Plastic Composite (WPC) is a material composed of wood fibers or flour and thermoplastic polymers, typically derived from recycled plastic.
The combination of these components results in a durable, versatile, and environmentally friendly material that finds applications in various industries, including construction.
WPC wall panels are an innovative application of this material, designed to provide both functional and aesthetic benefits to interior and exterior spaces.
The manufacturing process of WPC wall panels involves blending the wood fibers and plastic polymers, followed by shaping and molding to produce panels of different sizes and designs.
The use of recycled plastic in WPC production reduces the demand for new plastic materials, contributing to waste reduction and resource conservation.
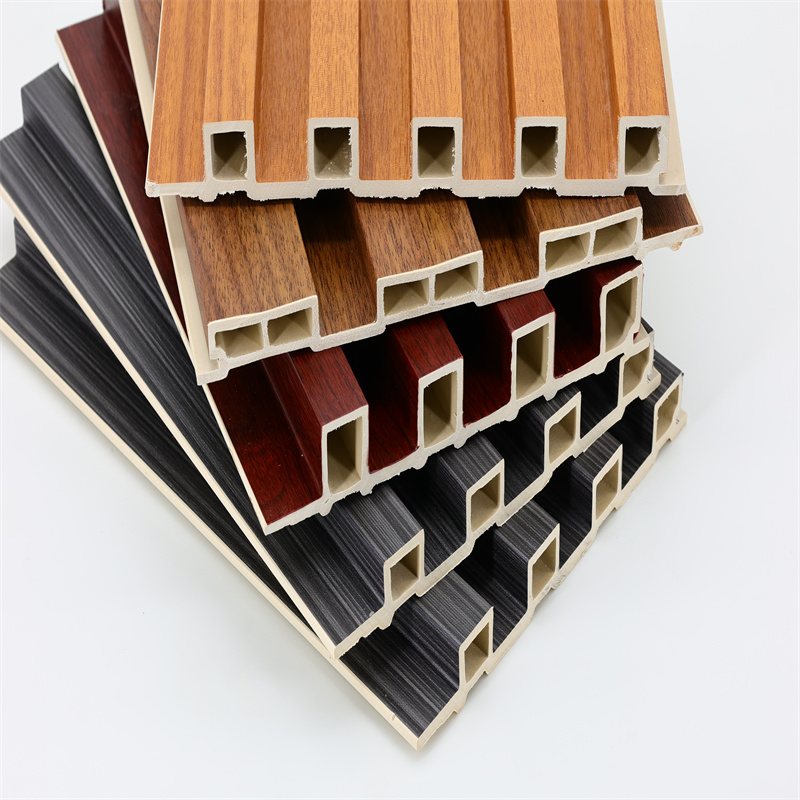

Eco-Friendly Features of WPC Wall Panels
2.1. Sustainable Material Sourcing
One of the key eco-friendly features of WPC wall panels is the use of recycled materials, particularly post-consumer and post-industrial plastic waste.
By incorporating plastic waste into the manufacturing process, these panels help divert plastic from landfills and reduce the environmental burden associated with its disposal.
Additionally, the utilization of wood fibers from sustainably managed forests ensures responsible sourcing practices, promoting biodiversity conservation.
2.2. Reduced Carbon Footprint
WPC wall panels boast a lower carbon footprint compared to traditional wood panels or other non-recycled plastic materials.
The production process consumes less energy and emits fewer greenhouse gases, making them a more environmentally responsible choice.
As carbon emissions remain a pressing global issue, adopting WPC wall panels can be a significant step towards mitigating climate change impacts.
2.3. Longevity and Durability
The longevity and durability of WPC wall panels further contribute to their sustainability.
These panels can withstand harsh weather conditions, resist decay, and require minimal maintenance throughout their lifespan.
By opting for durable materials, the need for frequent replacements is reduced, thus lowering overall resource consumption and waste generation.
The Economic Benefits of WPC Wall Panels
3.1. Cost-Effectiveness
WPC wall panels offer a cost-effective solution for interior and exterior cladding applications.
While their initial purchase cost may be slightly higher than traditional wood panels, their extended lifespan and reduced maintenance needs lead to long-term cost savings.
Property owners and developers can benefit from lower repair and replacement expenses over the building’s lifecycle.
3.2. Resource Efficiency
As WPC wall panels incorporate recycled materials, they contribute to a more resource-efficient economy.
By utilizing post-consumer plastics and sustainably sourced wood fibers, the demand for virgin materials is diminished, easing the strain on natural resources and fostering a circular economy approach.
3.3. Energy Efficiency
The manufacturing process of WPC wall panels requires less energy compared to traditional wood processing or the production of alternative materials like aluminum or steel.
The energy efficiency of WPC production translates to reduced operational costs for manufacturers and a smaller overall environmental impact.
Challenges and Future Prospects
4.1. Recycling and Waste Management
While WPC wall panels utilize recycled plastic, the end-of-life challenges of these panels need to be addressed.
Recycling WPC materials can be more complex than recycling single-stream plastics,
and proper waste management systems must be established to ensure that these panels do not end up in landfills at the end of their useful life.
4.2. Awareness and Market Penetration
The adoption of WPC wall panels is still relatively low compared to traditional materials.
Raising awareness among architects, builders, and consumers about the benefits of WPC, both environmentally and economically,
is crucial for increasing its market penetration and driving wider adoption in the construction industry.
Wood-Plastic Composite (WPC) wall panels offer a compelling case for sustainable and economical construction practices.
Through the use of recycled materials, reduced carbon footprint, and resource-efficient production processes, WPC wall panels contribute to environmental preservation and promote responsible building practices.
Their cost-effectiveness, longevity, and durability further enhance their appeal as a viable alternative to traditional wall paneling materials.
However, addressing recycling challenges and fostering greater awareness in the market are essential steps to fully realize
the potential of WPC wall panels in shaping a greener and more sustainable future for the construction industry.
By embracing these eco-friendly solutions, we can create a positive impact on the environment while building aesthetically pleasing and economically viable spaces for generations to come.